Question: Define the ng-content Directive?
Answer: Conventional HTML elements have some content between the tags. For instance:
<p>Put your paragraph here</p>Now consider the following example of having custom text between angular tags:
<app-work>This won’t work like HTML until you use ng-content Directive</app-work>However, doing so won’t work the way it worked for HTML elements. In order to make it work just like the HTML example mentioned above, we need to use the ng-content Directive. Moreover, it is helpful in building reusable components.
Know more about the ng-content directive.
Question: Please explain the various features of Angular.
Answer: There are several features of Angular that make it an ideal front end JavaScript framework. Most important of them are described as follows:
- Accessibility Applications
Angular allows creating accessible applications using ARIA-enabled components, built-in a11y test infrastructure, and developer guides.
- Angular CLI
Angular provides support for command-line interface tools. These tools can be used for adding components, testing, instant deploying, etc.
- Animation Support
Angular’s intuitive API allows the creation of high-performance, complex animation timelines with very little code.
- Cross-Platform App Development
Angular can be used for building an efficient and powerful desktop, native, and progressive web apps. Angular provides support for building native mobile applications using Cordova, Ionic, or NativeScript.
Angular allows creating high performance, offline, and zero-step installation progressive web apps using modern web platform capabilities. The popular JS framework can also be used for building desktop apps for Linux, macOS, and Windows.
- Code Generation
Angular is able to convert templates into highly-optimized code for modern JavaScript virtual machines.
- Code Splitting
With the new Component Router, Angular apps load quickly. The Component Router offers automatic code-splitting so that only the code required to render the view that is requested by a user is loaded.
- Synergy with Popular Code Editors and IDEs
Angular offers code completion, instant errors, etc. with popular source code editors and IDEs.
- Templates
Allows creating UI views with a simple and powerful template syntax.
- Testing
Angular lets you carry out frequent unit tests using Karma. The Protractor allows running faster scenario tests in a stable way.
Question: State some advantages of Angular over other frameworks.
Answer:
Out of box Features: Several built-in features like routing, state management, rxjs library, and HTTP services are straight out of the box services provided by Angular. So, one does not need to look for the above-stated features separately.
Declarative UI: Angular uses HTML to render the UI of an application as it is a declarative language and is much easier to use than JavaScript.
Long-term Google Support: Google plans to stick with Angular and further scale up its ecosystem as it has offered its long term support to Angular.
Question: What is the difference between Angular and AngularJS.
Answer:
| Parameters | AngularJS | Angular |
| Architecture | MVC or Model-View-Controller architecture facilitates the AngularJS framework, where the Model contains the business logic and Controllers processes information, lastly, View shows the information present in the Model. | Angular replaces controllers with Components that are directives with a predefined template. |
| Language | AngularJS uses JavaScript language, which is a dynamically typed language. | Angular uses TypeScript language, a statically typed language, and a superset of JavaScript. Angular provides better performance while developing larger applications. |
| Mobile Support | Does not support mobile support. | Supported by all popular mobile browsers. |
| Structure | The process of maintaining code becomes tedious in the case of larger applications. | It is easier to maintain code for larger applications as it provides a better structure. |
| Expression Syntax | A developer needs to remember the correct ng-directive for binding an event or a property. | Property binding is done using "[ ]" attribute and event binding is done using "( )" attribute. |
| Routing | AngularJS uses $routeprovider.when() | Angular uses @RouteConfig{(…)} |
| Speed | The development effort and time are reduced significantly because of the two-way data binding | Angular is faster due to upgraded features. |
| Dependency Injection | AngularJS doesn’t support DI. | Angular supports a hierarchical Dependency Injection with unidirectional tree-based change detection. |
| Support | No official support or updates are available for AngularJS. | Angular has active support with updates rolling out every now and then. |
Question: What are Lifecycle hooks in Angular? Explain some life cycles hooks
Answer: Angular components enter its lifecycle from the time it is created to the time it is destroyed. Angular hooks provide ways to tap into these phases and trigger changes at specific phases in a lifecycle.
ngOnChanges( ): This method is called whenever one or more input properties of the component changes. The hook receives a SimpleChanges object containing the previous and current values of the property.
ngOnInit( ): This hook gets called once, after the ngOnChanges hook.
It initializes the component and sets the input properties of the component.
ngDoCheck( ): It gets called after ngOnChanges and ngOnInit and is used to detect and act on changes that cannot be detected by Angular.
We can implement our change detection algorithm in this hook.
ngAfterContentInit( ): It gets called after the first ngDoCheck hook. This hook responds after the content gets projected inside the component.
ngAfterContentChecked( ): It gets called after ngAfterContentInit and every subsequent ngDoCheck. It responds after the projected content is checked.
ngAfterViewInit( ): It responds after a component's view, or a child component's view is initialized.
ngAfterViewChecked( ): It gets called after ngAfterViewInit, and it responds after the component's view, or the child component's view is checked.
ngOnDestroy( ): It gets called just before Angular destroys the component. This hook can be used to clean up the code and detach event handlers.
Question: Could we make an angular application to render on the server-side?
Answer: Yes, we can, with Angular Universal, a technology provided by Angular capable of rendering applications on the server-side.
The benefits of using Angular Universal are:
- Better User Experience: Allows users to see the view of the application instantly.
- Better SEO: Universal ensures that the content is available on every search engine leading to better SEO.
- Loads Faster: Render pages are available to the browsers sooner, so the server-side application loads faster.
Question: Explain Dependency Injection?
Answer: Dependency injection is an application design pattern that is implemented by Angular and forms the core concepts of Angular.
Let us understand in a detailed manner. Dependencies in Angular are services which have a functionality. Various components and directives in an application can need these functionalities of the service. Angular provides a smooth mechanism by which these dependencies are injected into components and directives.
Question: Describe the MVVM architecture.
Answer: MVVM architecture removes tight coupling between each component. The MVVM architecture comprises of three parts:
- Model
- View
- ViewModel
The architecture allows the children to have reference through observables and not directly to their parents.
- Model: It represents the data and the business logic of an application, or we may say it contains the structure of an entity. It consists of the business logic - local and remote data source, model classes, repository.
- View: View is a visual layer of the application, and so consists of the UI Code(in Angular- HTML template of a component.). It sends the user action to the ViewModel but does not get the response back directly. It has to subscribe to the observables which ViewModel exposes to it to get the response.
- ViewModel: It is an abstract layer of the application and acts as a bridge between the View and Model(business logic). It does not have any clue which View has to use it as it does not have a direct reference to the View. View and ViewModel are connected with data-binding so, any change in the View the ViewModel takes note and changes the data inside the Model. It interacts with the Model and exposes the observable that can be observed by the View.
Question: Demonstrate navigating between different routes in an Angular application.
Answer: Following code demonstrates how to navigate between different routes in an Angular app dubbed “Some Search App”:
import from "@angular/router";
.
.
.
@Component({
selector: 'app-header',
template: `
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" (click)="goHome()">Some Search App</a>
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" (click)="goHome()">Home</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" (click)="goSearch()">Search</a>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
`
})
class HeaderComponent {
constructor(private router: Router) {}
goHome() {
this.router.navigate(['']);
}
goSearch() {
this.router.navigate(['search']);
}
}Question: What is the AOT (Ahead-Of-Time) Compilation? What are its advantages?
Answer: An angular application consists of components and templates which a browser cannot understand. Therefore, every Angular application needs to be compiled before running inside the browser. The Angular compiler takes in the JS code, compiles it, and then produces some JS code. It is known as AOT compilation and happens only once per occasion per user.
There are two kinds of compilation that Angular provides:
JIT(Just-in-Time) compilation: the application compiles inside the browser during runtime
AOT(Ahead-of-Time) compilation: the application compiles during the build time.
Advantages of AOT compilation:
- Fast Rendering: The browser loads the executable code and renders it immediately as the application is compiled before running inside the browser.
- Fewer Ajax Requests: The compiler sends the external HTML and CSS files along with the application, eliminating AJAX requests for those source files.
- Minimizing Errors: Easy to detect and handle errors during the building phase.
- Better Security: Before an application runs inside the browser, the AOT compiler adds HTML and templates into the JS files, so there are no extra HTML files to be read, thus providing better security for the application.
Question: Could you explain services in Angular?
Answer: Singleton objects in Angular that get instantiated only once during the lifetime of an application are called services. An Angular service contains methods that maintain the data throughout the life of an application.
The primary intent of an Angular service is to organize as well as share business logic, models, or data and functions with various components of an Angular application.
The functions offered by an Angular service can be invoked from any Angular component, such as a controller or directive.
Question: Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of using Angular?
Answer: Following are the various advantages of using Angular:
- Ability to add a custom directive
- Exceptional community support
- Facilitates client and server communication
- Features strong features, such as Animation and Event Handlers
- Follows the MVC pattern architecture
- Offers support for static template and Angular template
- Support for two-way data-binding
- Supports dependency injection, RESTful services, and validations
Disadvantages of using Angular are enumerated as follows:
- Complex SPAs can be inconvenient and laggy to use due to their size
- Dynamic applications do not always perform well
- Learning Angular requires a decent effort and time
Question: Enumerate some salient features of Angular 7.
Answer: Unlike the previous versions of Angular, the 7th major release comes with splitting in @angular/core. This is done in order to reduce the size of the same. Typically, not each and every module is required by an Angular developer. Therefore, in Angular 7 each split of the @angular/core will have no more than 418 modules.
Also, Angular 7 brings drag-and-drop and virtual scrolling into play. The latter enables loading as well as unloading elements from the DOM. For virtual scrolling, the latest version of Angular comes with the package. Furthermore, Angular 7 comes with a new and enhanced version of the ng-compiler.
Question: What is string interpolation in Angular?
Answer: Also referred to as moustache syntax, string interpolation in Angular refers to a special type of syntax that makes use of template expressions in order to display the component data. These template expressions are enclosed within double curly braces i.e. {{ }}.
The JavaScript expressions that are to be executed by Angular are added within the curly braces and the corresponding output is embedded into the HTML code. Typically, these expressions are updated and registered like watches as a part of the digest cycle.
Question: Explain Angular Authentication and Authorization.
Answer: The user login credentials are passed to an authenticate API, which is present on the server. Post server-side validation of the credentials, a JWT (JSON Web Token) is returned. The JWT has information or attributes regarding the current user. The user is then identified with the given JWT. This is called authentication.
Post logging-in successfully, different users have a different level of access. While some may access everything, access for others might be restricted to only some resources. The level of access is authorization.
Here is a detailed post on Angular 7 - JWT Authentication Example & Tutorial: http://jasonwatmore.com/post/2018/11/16/angular-7-jwt-authentication-example-tutorial
Question: Can you explain the concept of scope hierarchy in Angular?
Answer: Angular organizes the $scope objects into a hierarchy that is typically used by views. This is known as the scope hierarchy in Angular. It has a root scope that can further contain one or several scopes called child scopes.
In a scope hierarchy, each view has its own $scope. Hence, the variables set by a view’s view controller will remain hidden to other view controllers. Following is a typical representation of a Scope Hierarchy:
- Root $scope
- $scope for Controller 1
- $scope for Controller 2
- …
- ..
- .
- $scope for Controller n
Question: How to generate a class in Angular 7 using CLI?
Answer:
ng generate class Dummy [options]This will generate a class named Dummy.
Question: Explain what is the difference between Angular and backbone.js?
Answer: Following are the various notable differences between Angular and Backbone.js
- Architecture
Backbone.js makes use of the MVP architecture and doesn’t offer any data binding process. Angular, on the contrary, works on the MVC architecture and makes use of two-way data binding for driving application activity.
- Community Support
Being backed by Google greatly ups the community support received by the Angular framework. Also, extensive documentation is available. Although Backbone.js has a good level of community support, it only documents on Underscore.js templates, not much else.
- Data Binding
Angular uses two-way data binding process and thus is a bit complex. Backbone.js, on the contrary, doesn’t have any data binding process and thus, has a simplistic API.
- DOM
The prime focus of Angular JS is upon valid HTML and dynamic elements that imitate the underlying data for rebuilding the DOM as per the specified rules and then works on the updated data records.
Backbone.js follows the direct DOM manipulation approach for representing data and application architecture changes.
- Performance
Thanks to its two-way data binding functionality, Angular offers an impactful performance for both small and large projects.
Backbone.js has a significant upper hand in performance over Angular in small data sets or small webpages. However, it is not recommended for larger webpages or large data sets due to the absence of any data binding process.
- Templating
Angular supports templating via dynamic HTML attributes. These are added to the document to develop an easy to understand application at a functional level. Unlike Angular, Backbone.js uses Underscore.js templates that aren’t fully-featured as Angular templates.
- The Approach to Testing
The approach to testing varies greatly between Angular and Backbone.js due to the fact that while the former is preferred for building large applications the latter is ideal for developing smaller webpages or applications.
For Angular, unit testing is preferred and the testing process is smoother through the framework. In the case of Backbone.js, the absence of a data binding process allows for a swift testing experience for a single page and small applications.
- Type
Angular is an open-source JS-based front-end web application framework that extends HTML with new attributes. On the other hand, Backbone.js is a lightweight JavaScript library featuring a RESTful JSON interface and MVP framework.
Question: How do Observables differ from Promises?
Answer: As soon as a promise is made, the execution takes place. However, this is not the case with observables because they are lazy. This means that nothing happens until a subscription is made. While promises handle a single event, observable is a stream that allows passing of more than one event. A callback is made for each event in an observable.
Question: Please explain the difference between Angular and AngularJS?
Answer: Various differences between Angular and AngularJS are stated as follows:
- Architecture - AngularJS supports the MVC design model. Angular relies on components and directives instead
- Dependency Injection (DI) - Angular supports a hierarchical Dependency Injection with unidirectional tree-based change detection. AngularJS doesn’t support DI
- Expression Syntax - In AngularJS, a specific ng directive is required for the image or property and an event. Angular, on the other hand, use () and [] for blinding an event and accomplishing property binding, respectively
- Mobile Support - AngularJS doesn’t have mobile support while Angular does have
- Recommended Language - While JavaScript is the recommended language for AngularJS, TypeScript is the recommended language for Angular
- Routing - For routing, AngularJS uses $routeprovider.when() whereas Angular uses @RouteConfig{(…)}
- Speed - The development effort and time are reduced significantly thanks to support for two-way data binding in AngularJS. Nonetheless, Angular is faster thanks to upgraded features
- Structure - With a simplified structure, Angular makes the development and maintenance of large applications easier. Comparatively, AngularJS has a less manageable structure
- Support - No official support or updates are available for the AngularJS. On the contrary, Angular has active support with updates rolling out every now and then
Question: Observe the following image:
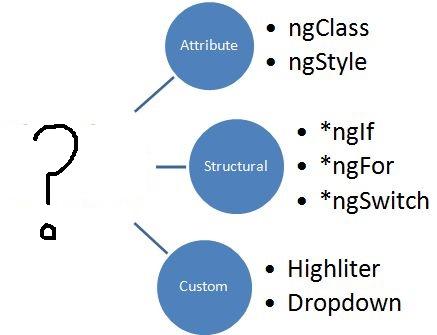
What should replace the “?”?
Answer: Directives. The image represents the types of directives in Angular; Attribute, structural, and custom.
Question: Could you explain the concept of templates in Angular?
Answer: Written with HTML, templates in Angular contains Angular-specific attributes and elements. Combined with information coming from the controller and model, templates are then further rendered to cater the user with the dynamic view.
Question: Explain the difference between an Annotation and a Decorator in Angular?
Answer: In Angular, annotations are used for creating an annotation array. They are only metadata set of the class using the Reflect Metadata library.
Decorators in Angular are design patterns used for separating decoration or modification of some class without changing the original source code.
Question: What are directives in Angular?
Answer: Directives are one of the core features of Angular. They allow an Angular developer to write new, application-specific HTML syntax. In actual, directives are functions that are executed by the Angular compiler when the same finds them in the DOM. Directives are of three types:
- Attribute Directives
- Component Directives
- Structural Directives
Question: What are the building blocks of Angular?
Answer: There are essentially 9 building blocks of an Angular application. These are:
- Components – A component controls one or more views. Each view is some specific section of the screen. Every Angular application has at least one component, known as the root component. It is bootstrapped inside the main module, known as the root module. A component contains application logic defined inside a class. This class is responsible for interacting with the view via an API of properties and methods.
- Data Binding – The mechanism by which parts of a template coordinates with parts of a component is known as data binding. In order to let Angular know how to connect both sides (template and its component), the binding markup is added to the template HTML.
- Dependency Injection (DI) – Angular makes use of DI to provide required dependencies to new components. Typically, dependencies required by a component are services. A component’s constructor parameters tell Angular about the services that a component requires. So, a dependency injection offers a way to supply fully-formed dependencies required by a new instance of a class.
- Directives – The templates used by Angular are dynamic in nature. Directives are responsible for instructing Angular about how to transform the DOM when rendering a template. Actually, components are directives with a template. Other types of directives are attribute and structural directives.
- Metadata – In order to let Angular know how to process a class, metadata is attached to the class. For doing so decorators are used.
- Modules – Also known as NgModules, a module is an organized block of code with a specific set of capabilities. It has a specific application domain or a workflow. Like components, any Angular application has at least one module. This is known as the root module. Typically, an Angular application has several modules.
- Routing – An Angular router is responsible for interpreting a browser URL as an instruction to navigate to a client-generated view. The router is bound to links on a page to tell Angular to navigate the application view when a user clicks on it.
- Services – A very broad category, a service can be anything ranging from a value and function to a feature that is required by an Angular app. Technically, a service is a class with a well-defined purpose.
- Template – Each component’s view is associated with its companion template. A template in Angular is a form of HTML tags that lets Angular know that how it is meant to render the component.
Question: Please explain the differences between Angular and jQuery?
Answer: The single biggest difference between Angular and jQuery is that while the former is a JS frontend framework, the latter is a JS library. Despite this, there are some similarities between the two, such as both features DOM manipulation and provides support for animation.
Nonetheless, notable differences between Angular and jQuery are:
- Angular has two-way data binding, jQuery does not
- Angular provides support for RESTful API while jQuery doesn’t
- jQuery doesn’t offer deep linking routing though Angular supports it
- There is no form validation in jQuery whereas it is present in Angular
Question: Could you explain the difference between Angular expressions and JavaScript expressions?
Answer: Although both Angular expressions and JavaScript expressions can contain literals, operators, and variables, there are some notable dissimilarities between the two. Important differences between Angular expressions and JavaScript expressions are enlisted below:
- Angular expressions support filters while JavaScript expressions do not
- It is possible to write Angular expressions inside the HTML tags. JavaScript expressions, contrarily, can’t be written inside the HTML tags
- While JavaScript expressions support conditionals, exceptions, and loops, Angular expressions don’t
Question: Can you give us an overview of Angular architecture?
Answer: You can draw some like this:
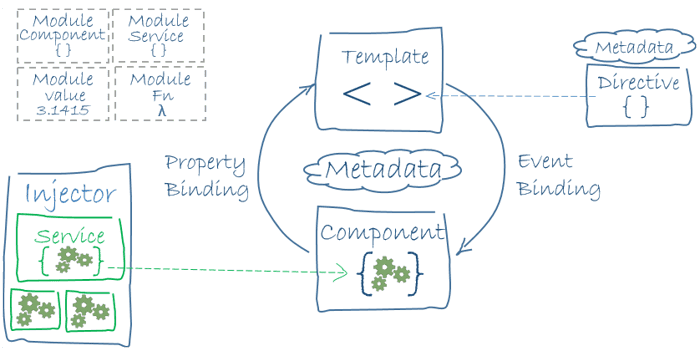
Here is Angular Architecture in detail: https://angular.io/guide/architecture
Question: What is Angular Material?
Answer: It is a UI component library. Angular Material helps in creating attractive, consistent, and fully functional web pages as well as web applications. It does so while following modern web design principles, including browser portability and graceful degradation.
Question: What is AOT (Ahead-Of-Time) Compilation?
Answer: Each Angular app gets compiled internally. The Angular compiler takes in the JS code, compiles it and then produces some JS code. This happens only once per occasion per user. It is known as AOT (Ahead-Of-Time) compilation.
Question: What is Data Binding? How many ways it can be done?
Answer: In order to connect application data with the DOM (Data Object Model), data binding is used. It happens between the template (HTML) and component (TypeScript). There are 3 ways to achieve data binding:
- Event Binding – Enables the application to respond to user input in the target environment
- Property Binding – Enables interpolation of values computed from application data into the HTML
- Two-way Binding – Changes made in the application state gets automatically reflected in the view and vice-versa. The ngModel directive is used for achieving this type of data binding.
Question: What is demonstrated by the arrow in the following image?
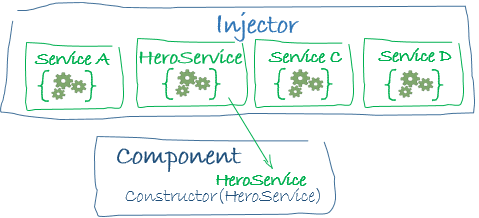
Answer: This represents a dependency injection or DI.
Question: Can you draw a comparison between the service() and the factory() functions?
Answer: Used for the business layer of the application, the service() function operates as a constructor function. The function is invoked at runtime using the new keyword.
Although the factory() function works in pretty much the same way as the service() function does, the former is more flexible and powerful. In actual, the factory() function are design patterns that help in creating objects.
Question: Please explain the digest cycle in Angular?
Answer: The process of monitoring the watchlist in order to track changes in the value of the watch variable is termed the digest cycle in Angular. The previous and present versions of the scope model values are compared in each digest cycle.
Although the digest cycle process gets triggered implicitly, it is possible to start it manually by using the $apply() function.
Question: Could you explain the various types of filters in AngularJS.
Answer: In order to format the value of expression so that it can be displayed to the user, AngularJS has filters. It is possible to add these filters to the controllers, directives, services, or templates. AngularJS also provides support for creating custom filters.
Organizing data in such a way so that it is displayed only when certain criteria are fulfilled is made possible using filters. Filters are added to the expressions using the pipe ‘|’ character. Various types of AngularJS filters are enumerated as follows:
- currency – Formats a number to the currency format
- date – Formats a data to some specific format
- filter – Selects a subset of items from an array
- json – Formats an object to a JSON string
- limitTo – Limits an array or string into a specified number of characters or elements
- lowercase – Formats a string to lowercase
- number – Formats a number to a string
- orderBy – Orders an array by an expression
Question: What is new in Angular 6?
Answer: Here are some of the new aspects introduced in Angular 6:
- Angular Elements – It allows converting Angular components into web components and embeds the same in some non-Angular application
- Tree Shakeable Provider – Angular 6 introduces a new way of registering a provider directly inside the @Injectable() decorator. It is achieved by using the providedIn attribute
- RxJS 6 – Angular 6 makes use of RxJS 6 internally
- i18n (internationalization) – Without having to build the application once per locale, any Angular application can have “runtime i18n”
Question: What is ngOnInit()? How to define it?
Answer: ngOnInit() is a lifecycle hook that is called after Angular has finished initializing all data-bound properties of a directive. It is defined as:
Interface OnInit {
ngOnInit() : void
}Question: What is SPA (Single Page Application) in Angular? Contrast SPA technology with traditional web technology?
Answer: In the SPA technology, only a single page, which is index.HTML, is maintained although the URL keeps on changing. Unlike traditional web technology, SPA technology is faster and easy to develop as well.
In conventional web technology, as soon as a client requests a webpage, the server sends the resource. However, when again the client requests for another page, the server responds again with sending the requested resource. The problem with this technology is that it requires a lot of time.
Question: What is the code for creating a decorator?
Answer: We create a decorator called Dummy:
function Dummy(target) {
dummy.log('This decorator is Dummy', target);
}Question: What is the process called by which TypeScript code is converted into JavaScript code?
Answer: It is called Transpiling. Even though TypeScript is used for writing code in Angular applications, it gets internally transpiled into equivalent JavaScript.
Question: What is ViewEncapsulation and how many ways are there do to do it in Angular?
Answer: To put simply, ViewEncapsulation determines whether the styles defined in a particular component will affect the entire application or not. Angular supports 3 types of ViewEncapsulation:
- Emulated – Styles used in other HTML spread to the component
- Native – Styles used in other HTML doesn’t spread to the component
- None – Styles defined in a component are visible to all components of the application
Question: Why prioritize TypeScript over JavaScript in Angular?
Answer: TypeScript is a superset of Javascript as it is Javascript + Types or extra features like typecasting for variables, annotations, variable scope and much more. The typescript is designed in a way to overcome Javascript shortcomings like typecasting of variables, classes, decorators, variable scope and many more. Moreover, Typescript is purely object-oriented programming that offers a "Compiler" that can convert to Javascript-equivalent code.
Question: Discuss the lifecycle designed for directive and components in Angular JS especially for the newly introduced version 6.0?
Answer:
Components and directive of Angular JS follow the following typical lifecycle.
- nhOnInit
- ngDoCheck
- ngOnDestroy
- Constructor
- ngOnChanges
- ngAfterContentInit (only for components)
- ngAfterContentChecked (only for components)
- ngAfterViewInit (only for components)
- ngAfterViewChecked (only for components)
Question: Write the features for Angular 6 over Angular 5.
Answer: Following are the features:
1. Added ng update
CLI command updates angular project dependencies to their latest versions. The ng update is a normal package manager tool to identify and update in normal package manager tools to identify and update other dependencies.
2. Uses RxJS6
This is the third party library (RxJS) and introduces two important changes as compared to RxJS5.
- Introduces a new internal package structure.
- Operator concept
To update of RxJS6, run the following command:
npm install --save rxjs@6To update your existing Angular Project, run the following:
npm install --save rxjs-compat3. The <ng-template>
Angular 6 uses <ng-template> instead of <template>
4. Service Level Changes
If in an earlier version, the user wanted to provide a service to the entire application, the user was required to add it to providers in the AppModule but it is not required in the case of Angular6.
5. Renamed Operators
Angular 6 has renamed following operators:
- do() => tap()
- catch() => catchError()
- finally() => finalize()
- switch()=>switchAll()
- throw() => throwError
Question: Why was Angular introduced as a client-side framework?
Answer: Traditionally, VanillaJS and jQuery were used by developers to develop dynamic websites. As the websites became more complex with added features and functionality, it was hard for the developers to maintain the code. Moreover, there was no provision of data handling facilities across the views by jQuery. So, Angular was built to address these issues, thus, making it easier for the developers by dividing code into smaller bits of information that are known as Components in Angular. Client-side frameworks permit the development of advanced web applications like SPAs which, if developed by VanillaJS, is a slower process.
Question: State some advantages of Angular over other frameworks.
Answer:
- Out of box Features: Several built-in features like routing, state management, rxjs library, and HTTP services are straight out of the box services provided by Angular. So, one does not need to look for the above-stated features separately.
- Declarative UI: Angular uses HTML to render the UI of an application as it is a declarative language and is much easier to use than JavaScript.
- Long-term Google Support: Google plans to stick with Angular and further scale up its ecosystem as it has offered its long term support to Angular.
Question: What is the difference between Angular and AngularJS.
Answer:
| Parameters | AngularJS | Angular |
| Architecture | MVC or Model-View-Controller architecture facilitates the AngularJS framework, where the Model contains the business logic and Controllers processes information, lastly, View shows the information present in the Model. | Angular replaces controllers with Components that are directives with a predefined template. |
| Language | AngularJS uses JavaScript language, which is a dynamically typed language. | Angular uses TypeScript language, a statically typed language, and a superset of JavaScript. Angular provides better performance while developing larger applications. |
| Mobile Support | Does not support mobile support. | Supported by all popular mobile browsers. |
| Structure | The process of maintaining code becomes tedious in the case of larger applications. | It is easier to maintain code for larger applications as it provides a better structure. |
| Expression Syntax | A developer needs to remember the correct ng-directive for binding an event or a property. | Property binding is done using "[ ]" attribute and event binding is done using "( )" attribute. |
| Routing | AngularJS uses $routeprovider.when() | Angular uses @RouteConfig{(…)} |
| Speed | The development effort and time are reduced significantly because of the two-way data binding | Angular is faster due to upgraded features. |
| Dependency Injection | AngularJS doesn’t support DI. | Angular supports a hierarchical Dependency Injection with unidirectional tree-based change detection. |
| Support | No official support or updates are available for AngularJS. | Angular has active support with updates rolling out every now and then. |
Question: What is the AOT (Ahead-Of-Time) Compilation? What are its advantages?
Answer: An angular application consists of components and templates which a browser cannot understand. Therefore, every Angular application needs to be compiled before running inside the browser. The Angular compiler takes in the JS code, compiles it, and then produces some JS code. It is known as AOT compilation and happens only once per occasion per user. There are two kinds of compilation that Angular provides:
- JIT(Just-in-Time) compilation: The application compiles inside the browser during runtime
- AOT(Ahead-of-Time) compilation: The application compiles during the build time.
Advantages of AOT compilation:
- Fast Rendering: The browser loads the executable code and renders it immediately as the application is compiled before running inside the browser.
- Fewer Ajax Requests: The compiler sends the external HTML and CSS files along with the application, eliminating AJAX requests for those source files.
- Minimizing Errors: Easy to detect and handle errors during the building phase.
- Better Security: Before an application runs inside the browser, the AOT compiler adds HTML and templates into the JS files, so there are no extra HTML files to be read, thus providing better security for the application.
Question: What are Lifecycle hooks in Angular? Explain some life cycles hooks.
Answer: Angular components enter its lifecycle from the time it is created to the time it is destroyed. Angular hooks provide ways to tap into these phases and trigger changes at specific phases in a lifecycle.
- ngOnChanges(): This method is called whenever one or more input properties of the component changes. The hook receives a SimpleChanges object containing the previous and current values of the property.
- ngOnInit(): This hook gets called once, after the ngOnChanges hook.
- It initializes the component and sets the input properties of the component.
- ngDoCheck(): It gets called after ngOnChanges and ngOnInit and is used to detect and act on changes that cannot be detected by Angular.
- We can implement our change detection algorithm in this hook.
- ngAfterContentInit(): It gets called after the first ngDoCheck hook. This hook responds after the content gets projected inside the component.
- ngAfterContentChecked(): It gets called after ngAfterContentInit and every subsequent ngDoCheck. It responds after the projected content is checked.
- ngAfterViewInit(): It responds after a component's view, or a child component's view is initialized.
- ngAfterViewChecked(): It gets called after ngAfterViewInit, and it responds after the component's view, or the child component's view is checked.
- ngOnDestroy(): It gets called just before Angular destroys the component. This hook can be used to clean up the code and detach event handlers.
Question: Could we make an angular application to render on the server-side?
Answer: Yes, we can, with Angular Universal, a technology provided by Angular capable of rendering applications on the server-side. The benefits of using Angular Universal are:
- Better User Experience: Allows users to see the view of the application instantly.
- Better SEO: Universal ensures that the content is available on every search engine leading to better SEO.
- Loads Faster: Render pages are available to the browsers sooner, so the server-side application loads faster.
Question: Explain Dependency Injection?
Answer: Dependency injection is an application design pattern that is implemented by Angular and forms the core concepts of Angular. Let us understand in a detailed manner. Dependencies in Angular are services which have a functionality. Various components and directives in an application can need these functionalities of the service. Angular provides a smooth mechanism by which these dependencies are injected into components and directives.
Question: Describe the MVVM architecture.
Answer: MVVM architecture removes tight coupling between each component. The MVVM architecture comprises of three parts:
- Model
- View
- ViewModel
The architecture allows the children to have reference through observables and not directly to their parents.
- Model: It represents the data and the business logic of an application, or we may say it contains the structure of an entity. It consists of the business logic - local and remote data source, model classes, repository.
- View: View is a visual layer of the application, and so consists of the UI Code(in Angular- HTML template of a component.). It sends the user action to the ViewModel but does not get the response back directly. It has to subscribe to the observables which ViewModel exposes to it to get the response.
- ViewModel: It is an abstract layer of the application and acts as a bridge between the View and Model(business logic). It does not have any clue which View has to use it as it does not have a direct reference to the View. View and ViewModel are connected with data-binding so, any change in the View the ViewModel takes note and changes the data inside the Model. It interacts with the Model and exposes the observable that can be observed by the View.
No comments:
Post a Comment