@ExceptionHandler
@ExceptionHandler works at the Controller level and it is only active for that particular Controller, not globally for the entire application.HandlerExceptionResolver
This will resolve any exception thrown by the application. It is used to resolve standard Spring exceptions to their corresponding HTTP Status Codes. It does not have control over the body of the response, means it does not set anything to the body of the Response.It does map the status code on the response but the body is null.
@ControllerAdvice
@ControllerAdvice used for global error handling in the Spring MVC application.It also has full control over the body of the response and the status code.👉Q: @Resource vs @Autowired
The primary difference is,
@Autowired is a spring annotation. Whereas @Resourceis specified by the JSR-250, as you pointed out yourself. So the latter is part of Java whereas the former is Spring specific.
Hence, you are right in suggesting that, in a sense. I found folks use
@Autowiredwith @Qualifier because it is more powerful. Moving from some framework to some other is considered very unlikely, if not myth, especially in the case of Spring.👉Q : Spring Boot vs Spring MVC vs Spring - How do they compare?
Spring Framework
Most important feature of Spring Framework is Dependency Injection. At the core of all Spring Modules is Dependency Injection or IOC Inversion of Control.
When DI or IOC is used properly, we can develop loosely coupled applications. And loosely coupled applications can be easily unit tested.
Spring MVC
Spring MVC Framework provides decoupled way of developing web applications. With simple concepts like Dispatcher Servlet, ModelAndView and View Resolver, it makes it easy to develop web applications.
Spring Boot
The problem with Spring and Spring MVC is the amount of configuration that is needed.
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:resources mapping="/webjars/**" location="/webjars/"/>
Spring Boot solves this problem through a combination of Auto Configuration and Starter Projects. Spring Boot also provide a few non functional features to make building production ready applications faster.
For complete answer with code examples refer - 👉Spring Boot vs Spring vs Spring MVC
Q : What is Auto Configuration?
The problem with Spring and Spring MVC is the amount of configuration that is needed.
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:resources mapping="/webjars/**" location="/webjars/"/>
Can we bring more intelligence into this? When a spring mvc jar is added into an application, can we auto configure some beans automatically?
Spring Boot looks at a) Frameworks available on the CLASSPATH b) Existing configuration for the application. Based on these, Spring Boot provides basic configuration needed to configure the application with these frameworks. This is called Auto Configuration.
For complete answer with code examples refer 👉Auto Configuration.
👉Q : What are Spring Boot Starter Projects?
Starters are a set of convenient dependency descriptors that you can include in your application. You get a one-stop-shop for all the Spring and related technology that you need, without having to hunt through sample code and copy paste loads of dependency descriptors.
For example, if you want to get started using Spring and JPA for database access, just include the spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependency in your project, and you are good to go.
👉Q : Can you explain more about Starters with an example?
Let’s consider an example starter - Spring Boot Starter Web.
If you want to develop a web application or an application to expose restful services, Spring Boot Start Web is the starter to pick. Lets create a quick project with Spring Boot Starter Web using Spring Initializr.
Dependency for Spring Boot Starter Web
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
Following screenshot shows the different dependencies that are added in to our application
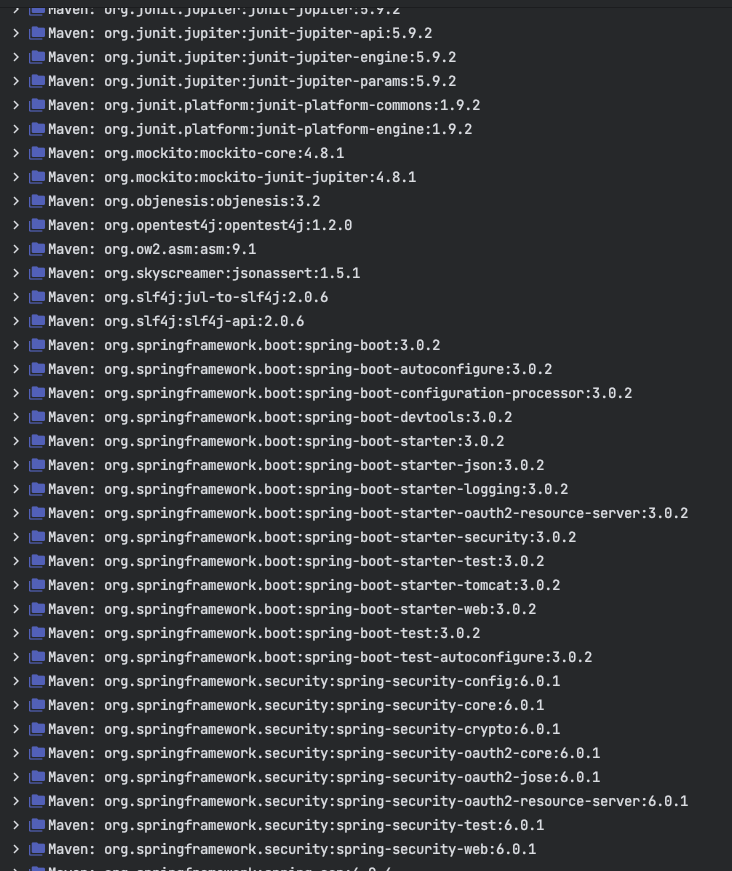
Dependencies can be classified into:
- Spring - core, beans, context, aop
- Web MVC - (Spring MVC)
- Jackson - for JSON Binding
- Validation - Hibernate Validator, Validation API
- Embedded Servlet Container - Tomcat
- Logging - logback, slf4j
Any typical web application would use all these dependencies. Spring Boot Starter Web comes pre packaged with these.
As a developer, I would not need to worry about either these dependencies or their compatible versions.
👉Q : What are the other Starter Project Options that Spring Boot provides?
Spring Boot also provides other starter projects including the typical dependencies to develop specific type of applications
- spring-boot-starter-web-services - SOAP Web Services
- spring-boot-starter-web - Web & RESTful applications
- spring-boot-starter-test - Unit testing and Integration Testing
- spring-boot-starter-jdbc - Traditional JDBC
- spring-boot-starter-hateoas - Add HATEOAS features to your services
- spring-boot-starter-security - Authentication and Authorization using Spring Security
- spring-boot-starter-data-jpa - Spring Data JPA with Hibernate
- spring-boot-starter-data-rest - Expose Simple REST Services using Spring Data REST
👉Q : How does Spring enable creating production ready applications in quick time?
Spring Boot aims to enable production ready applications in quick time. Spring Boot provides a few non functional features out of the box like caching, logging, monitoring and embedded servers.
- spring-boot-starter-actuator - To use advanced features like monitoring & tracing to your application out of the box
- spring-boot-starter-undertow, spring-boot-starter-jetty, spring-boot-starter-tomcat - To pick your specific choice of Embedded Servlet Container
- spring-boot-starter-logging - For Logging using logback
- spring-boot-starter-cache - Enabling Spring Framework’s caching support
What is the minimum baseline Java Version for Spring Boot 2 and Spring 5?
Spring Boot 2.0 requires Java 8 or later. Java 6 and 7 are no longer supported.
Recommended Reading
- https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.0.0-M1-Release-Notes
👉Q : What is the easiest approach to create a Spring Boot Project?
Spring Initializr http://start.spring.io/ is great tool to bootstrap your Spring Boot projects.
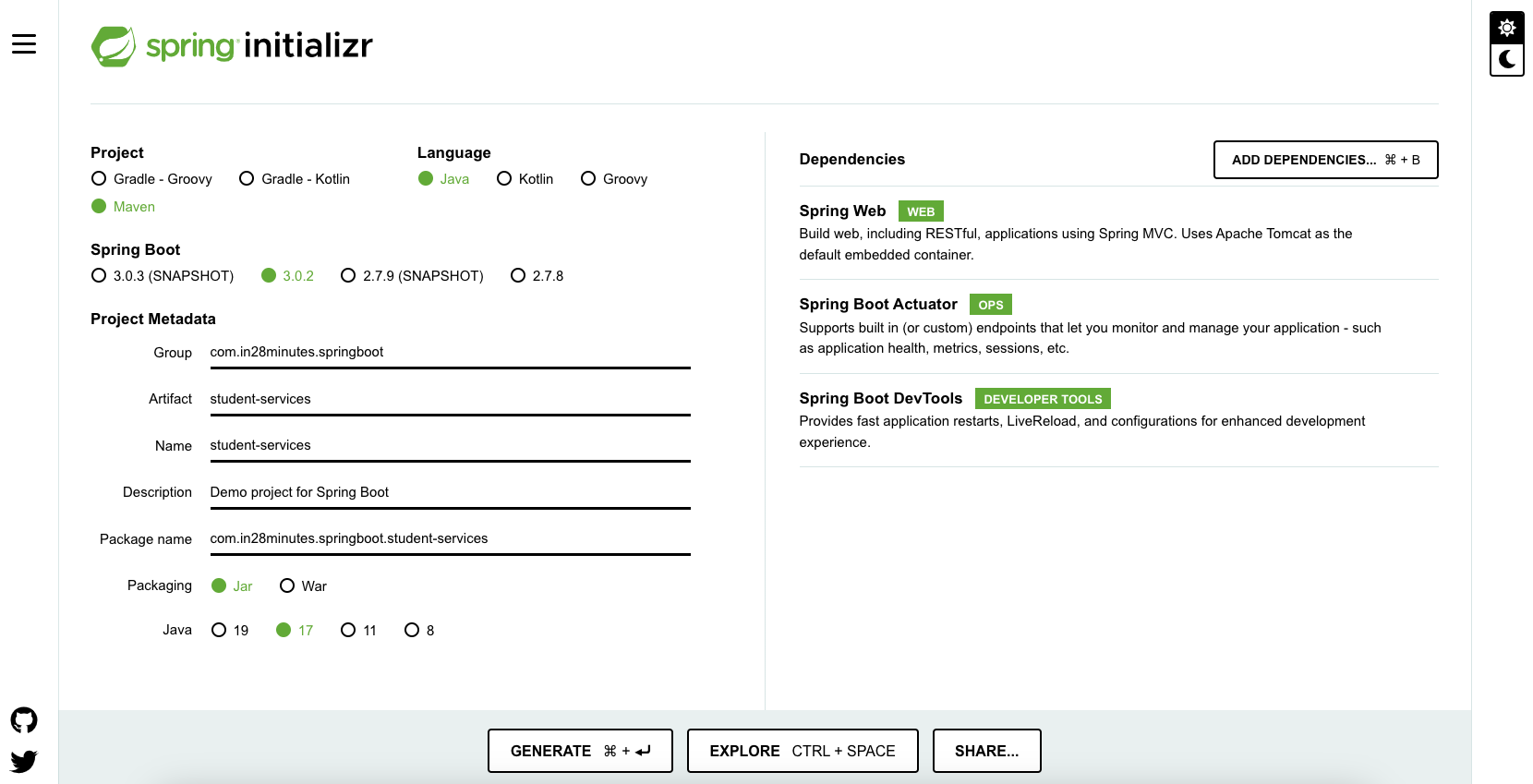
As shown in the image above, following steps have to be done
- Launch Spring Initializr and choose the following
- Choose
com.in28minutes.springbootas Group - Choose
student-servicesas Artifact - Choose following dependencies
- Web
- Actuator
- DevTools
- Choose
- Click Generate Project.
- Import the project into Eclipse. File -> Import -> Existing Maven Project.
Q : Is Spring Initializr the only way to create Spring Boot Projects?
No.
Spring Initializr makes it easy to create Spring Boot Projects. But you can setup a maven project and add the right dependencies to start off.
In our Spring course, we use 2 approaches to create projects.
- The first one is start.spring.io.
- The other one - setting up a project manually is used in the Section titled - “Basic Web Application”
Setting up a maven project manually
Here are the important steps:
- In Eclipse, Use File -> New Maven Project to create a new project.
- Add dependencies.
- Add the maven plugins!
- Add the Spring Boot Application class
You are ready to go!
Q : Why do we need spring-boot-maven-plugin?
spring-boot-maven-plugin provides a few commands which enable you to package the code as a jar or run the application
- spring-boot:run runs your Spring Boot application.
- spring-boot:repackage repackages your jar/war to be executable.
- spring-boot:start and spring-boot:stop to manage the lifecycle of your Spring Boot application (i.e. for integration tests).
- spring-boot:build-info generates build information that can be used by the Actuator.
Q : How can I enable auto reload of my application with Spring Boot?
Use Spring Boot Developer Tools.
Adding Spring Boot Developer Tools to your project is very simple.
Add this dependency to your Spring Boot Project pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Restart the application.
You are all Set.
If you would want to auto load the page as well, you can look at LiveReload
- http://www.logicbig.com/tutorials/spring-framework/spring-boot/boot-live-reload/.
In my trials, we found LiveReload buggy. Do let us know if you have a better experience with it.
Q : What and Why Embedded Servers?
Think about what you would need to be able to deploy your application (typically) on a virtual machine.
- Step 1 : Install Java
- Step 2 : Install the Web/Application Server (Tomcat/Websphere/Weblogic etc)
- Step 3 : Deploy the application war
What if we want to simplify this?
How about making the server a part of the application?
You would just need a virtual machine with Java installed and you would be able to directly deploy the application on the virtual machine. Isn’t it cool?
This idea is the genesis for Embedded Servers.
When we create an application deployable, we would embed the server (for example, tomcat) inside the deployable.
For example, for a Spring Boot Application, you can generate an application jar which contains Embedded Tomcat. You can run a web application as a normal Java application!
Embedded server is when our deployable unit contains the binaries for the server (example, tomcat.jar).
Q : How can I add custom JS code with Spring Boot?
Create a folder called static under resources folder. You can put your static content in that folder.
For your example the path to myapp.js would be resources\static\js\myapp.js
You can refer to it in jsp using
<script src="/js/myapp.js"></script>
Error : HAL browser gives me unauthorized error - Full authentication is required to access this resource. How can I fix it?
{
"timestamp": 1488656019562,
"status": 401,
"error": "Unauthorized",
"message": "Full authentication is required to access this resource.",
"path": "/beans"
}
Two options
Option 1 : Disable security
application.properties
management.security.enabled: FALSE
Option 2 : Search for password in the log and pass it in the request header
Q : What is Spring Data?
From http://projects.spring.io/spring-data/
Spring Data’s mission is to provide a familiar and consistent, Spring-based programming model for data access while still retaining the special traits of the underlying data store. It makes it easy to use data access technologies, relational and non-relational databases, map-reduce frameworks, and cloud-based data services.
To make it simpler, Spring Data provides Abstractions (interfaces) you can use irrespective of underlying data source.
An example is shown below
interface TodoRepository extends CrudRepository<Todo, Long> {
You can define a simple repository and use it to insert, update, delete and retrieve todo entities from the database - without writing a lot of code.
Q : What is Spring Data REST?
Spring Data REST can be used to expose HATEOAS RESTful resources around Spring Data repositories.
An example using JPA is shown below
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "todos", path = "todos")
public interface TodoRepository
extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Todo, Long> {
Without writing a lot of code, we can expose RESTful API around Spring Data Repositories.
A few example REST Services are shown below:
POST
- URL : http://localhost:8080/todos
- Use Header : Content-Type:application/json
- Request Content
{
"user": "Jill",
"desc": "Learn Hibernate",
"done": false
}
Response Content
{
"user": "Jill",
"desc": "Learn Hibernate",
"done": false,
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
},
"todo": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/todos/1"
}
}
}
The response contains the href of the newly created resource.
Q : How does path=”users”, collectionResourceRel=”users” work with Spring Data Rest?
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "users", path = "users")
public interface UserRestRepository extends
PagingAndSortingRepository<User, Long>
- path - The path segment under which this resource is to be exported.
- collectionResourceRel - The rel value to use when generating links to the collection resource. This is used when generating HATEOAS links.
Q : What happens in the background when a Spring Boot Application is “Run as Java Application”?
If you are using Eclipse IDE, Eclipse maven plugin ensures that as soon as you add a dependency or make a change to the class file, it is compiled and ready in the target folder! And after that its just like any other Java application.
When you launch the java application, then the spring boot auto configuration magic kicks in.
- It launches up tomcat when it sees that you are developing a web application!
Q : Can we use jetty instead of tomcat in spring-boot-starter-web?
Remove the existing dependency on spring-boot-starter-web and add these in.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
Q : How to generate a WAR file with Spring Boot?
Recommended Reading
- https://spring.io/guides/gs/convert-jar-to-war/
Here’s the direct link to spring documentation
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#build-tool-plugins-maven-packaging
Q : How to deploy to a different server with with Spring Boot?
You would need to do 2 Steps
- Generate a war from the project.
- Deploy it to your favourite server (Websphere or Weblogic or Tomcat or …).
Step 1 : This getting started guide should help - https://spring.io/guides/gs/convert-jar-to-war/
Step 2 : Depends on your server
Q : What is the difference between RequestMapping and GetMapping?
- RequestMapping is generic - you can use with GET, POST, PUT or any of the other request methods using the method attribute on the annotation.
- GetMapping is specific to GET request method. It’s just an extension of RequestMapping to improve clarity.
Q : Why do we recommend not to use Spring Data Rest in real world applications?
We think Spring Data Rest is Good for quick prototyping! Be cautious about using this in Big applications!
With Spring Data REST you are exposing your database entitities directly as REST Services.
When you design RESTful services, Best design practices suggests that your interface should consider two important things
- Your Domain Model
- Your Consumers
With Spring Data REST, you are not considering either of those. You just expose entities as REST Services.
Thats why we suggest to use it for quick prototyping or the initial evolution of a project. It may not be a great idea for a fully evolved project.
Q : How do I change the package name of a project in Spring Initializer?
Good news is you can customise it. Click the link “Switch to the full version.“. You would be able to configure the package name you would want!
Q : Where can I find the complete list of properties that can be configured in application.properties?
Here’s the complete guide
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/common-application-properties.html
Q : What is the difference between JPA and Hibernate?
Short Story
- JPA is a specification/Interface
- Hibernate is one of JPA implementations
When we use JPA, we use the annotation and interfaces from javax.persistence package, without using the hibernate import packages.
We recommend using JPA annotations as we are not tied to Hibernate as implementation. Later (I know - <1% Chance), we can use another JPA implementation.
Q : In which layer, should the boundary of a transaction start?
We recommend managing transactions in the Service layer. Logic for business transactions is in the business/service layer and you would want to enforce transaction management at that level.
Q : What are the dependencies needed to start up a JPA Application connecting to in memory database H2 with Spring Boot?
In a Spring Boot project, you should be able to launch up H2 Console as long as you ensure the following dependencies are on the class path.
- web starter
- h2
- data jpa starter
The exact dependencies are shown below:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
A few tips:
- An in-memory database is live only during the time of execution of the application. It is an efficient way to learn a framework.
- This is not how you want your real world applications to behave.
- We explain how to connect to a database of your choice in the answer to the question “How do we connect to a external database?”.
Q : How is Hibernate chosen as the default implementation for JPA without any configuration?
Because of Spring Boot Auto Configuration.
This is the dependency we added in
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
The Starter spring-boot-starter-data-jpa has a transitive dependency on Hibernate and JPA.
When Spring Boot sees Hibernate in the class path, it auto configures it as the default JPA Implementation.
Q : Where is the database connection info specified? How does it know to automatically connect to H2?
Thats Spring Boot Autoconfiguration magic.
From https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-boot-auto-configuration.html
Spring Boot auto-configuration attempts to automatically configure your Spring application based on the jar dependencies that you have added. For example, If HSQLDBis on your classpath, and you have not manually configured any database connection beans, then we will auto-configure an in-memory database
More Reading
- http://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-auto-configuration
Q : How do we connect to a external database like MSSQL or oracle?
Let’s consider one of those as an example - MySQL
Step 1 - Add dependency for mqsql connector to pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
Step 2 - Remove H2 Dependency from pom.xml
Or atleast make its scope as test
<!--
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
-->
Step 3 - Setup your My SQL Database
- For more check out - https://github.com/in28minutes/jpa-with-hibernate#installing-and-setting-up-mysql
Step 4 - Configure your connection to My SQL Database
Configure application.properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/todo_example
spring.datasource.username=todouser
spring.datasource.password=YOUR_PASSWORD
Step 5 - Restart and You are ready!
That’s it
Q : What is the default h2 database name configured by Spring Boot? Why is the default database name testdb?
This is where all the default values in application.properties are listed
- https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/common-application-properties.html
Look for the property below
spring.datasource.name=testdb # Name of the datasource.
If you are using an H2 in-memory database, thats exactly the name that Spring Boot uses to setup your H2 database.
Q : What happens if H2 is not in the classpath?
You get this error
Cannot determine embedded database driver class for database type NONE
Add H2 to the pom.xml and Restart your server
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Q : Can you give an example for ReadOnly as true in Transaction management?
- When you read stuff from the database, user details or any other details, you wanna set read only on the transaction so that Hibernate does not need to check for changes to the entities. This is more efficient.
Q : What is best way to expose custom application configuration with Spring Boot?
The problem with @Value is that you would have your configuration values distributed through out your application. A better option would be to have a centralized approach.
You can define a configuration component using
@ConfigurationProperties.@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("basic")
public class BasicConfiguration {
private boolean value;
private String message;
private int number;
The values can be configured in application.properties
basic.value: true
basic.message: Dynamic Message
basic.number: 100
Q : What is the need for Profiles?
Enterprise application development is complex. You have multiple environments
- Dev
- QA
- Stage
- Production
You want to have different application configuration in each of the environments.
Profiles help to have different application configuration for different environments.
Spring and Spring Boot provide features where you can specify
- What is the configuration for various environments in different profiles?
- Set the active profile for a specific environment.
Spring Boot would pick up the application configuration based on the active profile that is set in a specific environment.
Q : How can you use profiles to configure environment specific configuration with Spring Boot?
Profile is nothing but a key to identify an environment.
In this example, we will use two profiles
- dev
- prod
The default application configuration is present in application.properties. Let’s consider an example.
application.properties
basic.value= true
basic.message= Dynamic Message
basic.number= 100
We would want to customize the application.properties for dev profile. We would need to create a file with name application-dev.properties and override the properties that we would want to customize.
application-dev.properties
basic.message: Dynamic Message in DEV
Similarly you can configure properties for prod profile.
application-prod.properties
basic.message: Dynamic Message in Prod
Once you have profile specific configuration, you would need to set the active profile in an environment.
There are multiple ways of doing this
- Using -Dspring.profiles.active=prod in VM Arguments
- Use
spring.profiles.active=prodin application.properties